Solutions
DVB specifications are used on every continent and in every country, with more than 1.5 billion DVB receivers in use.
The work of the DVB Project has resulted in a comprehensive list of technical and non-technical documents describing solutions required by the market to make the best use of digital broadcasting technology.
DVB standards support a wide variety of television use cases and solutions.
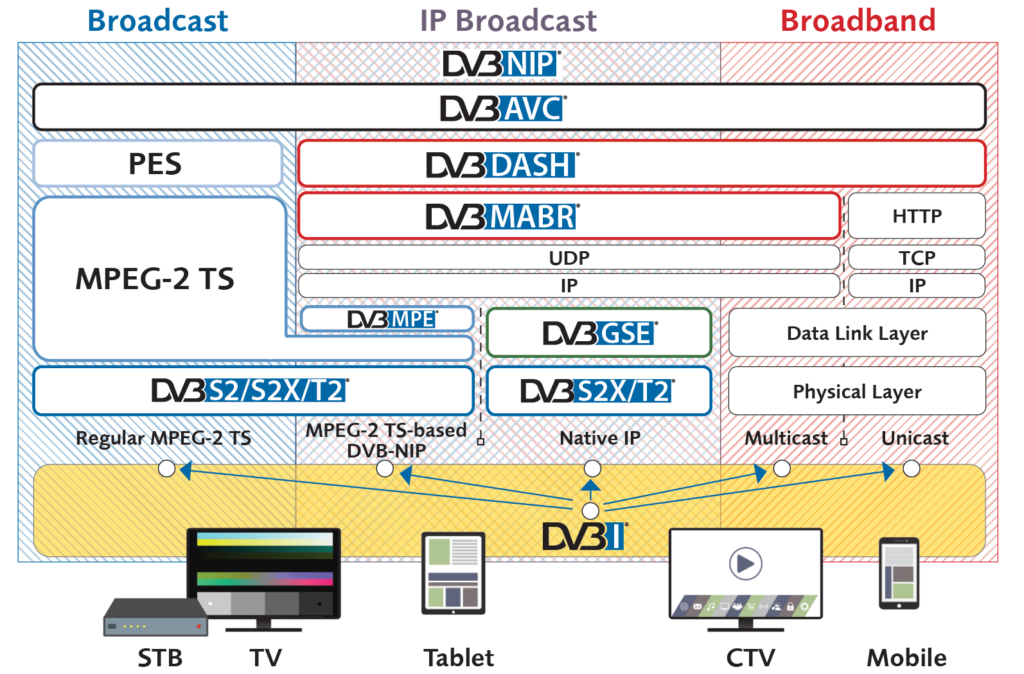
As shown above, DVB-I underpins DVB’s vision of a truly converged media delivery ecosystem targeting the full range of end-user devices.
IP-based delivery is handled via broadcast, multicast and unicast networks, combined seamlessly with existing MPEG-2 Transport Stream-based broadcast networks.
DVB’s audio and video coding specification (DVB-AVC) provides a further layer of interoperability, benefiting manufacturers, operators and end users alike.
Key to diagram
DVB-NIP: Native IP broadcasting
DVB-AVC: Specification for the use of Video and Audio Coding in
Broadcast and Broadband Applications
PES: Packetized Elementary Stream
DVB-DASH: (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP) DVB MPEG-DASH Profile for Transport of ISO BMFF Based DVB Services over IP Based Networks
MPEG-2 TS: MPEG-2 Transport Stream
DVB-MABR: (Multicast Adaptive Bit Rate) Adaptive media streaming over IP multicast
HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol
UDP: User Datagram Protocol
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
IP: Internet Protocol
DVB-MPE: Multi-Protocol Encapsulation
DVB-GSE: Generic Stream Encapsulation
DVB-I: Internet-based service discovery and programme information
